As the name implies, a temperature controller is an instrument used to control temperatures, mainly without extensive operator involvement. A controller in a temperature control system will accept a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD as input and compare the actual temperature to the desired control temperature, or setpoint. It will then provide an output to a control element.
Digital temperature controllers are used in a variety of applications, ranging from industrial processes to consumer products. For example, industrial applications such as HVAC systems, food processing, and chemical processing often require precise temperature control in order to ensure quality and safety. On the other hand, consumer products such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and water heaters also rely on temperature controllers to maintain a comfortable environment.
Why Are Temperature Controllers Important?
Temperature controllers are essential for ensuring optimal performance and safety in both industrial equipment and consumer products. They are needed in any application where a specific process temperature is required to be stable. For example, in the food industry, temperature controllers are critical for preserving food safety standards as they help to maintain a consistent and safe temperature range in refrigeration equipment to prevent food spoilage and contamination.There are two types of temperature control: open loop control and closed loop control. Open loop control is a type of control system in which the output of the system is not monitored or fed back to the input. This means that the system is not self-regulating and is prone to error over time. Closed loop control, on the other hand, is a type of control system in which the output is monitored and fed back to the input. This allows the system to make adjustments as needed in order to keep the output within a desired range. This makes the system self-regulating and much less prone to error over time.
Different Types of Temperature Controllers
There are three basic types of process controllers:On/Off Controllers
On/Off control is a type of control system in which the output of a system is either completely on or completely off – with no middle state. This type of basic temperature controller is typically used in applications where a binary response is required; the output is either fully activated or fully deactivated. In this type of system, the control output is either a discrete value (On/Off) or a continuous value (open/closed). On/Off control systems are useful for regulating temperature, pressure, and flow rate in industrial settings. On/Off control is usually used where a precise control is not necessary, in systems which cannot handle having the energy turned on and off frequently, where the mass of the system is so great that temperatures change extremely slowly, or for a temperature alarm. One special type of On/Off control used for alarm is a limit controller. This type of controller uses a latching relay, which must be manually reset, and is used to shut down a process when a certain temperature is reached.Proportional Controllers
Proportional control is a type of feedback control system that is used to maintain a desired set point by adjusting the output based on the error between the set point and the actual output. This type of control is widely used because it is simple to implement and his highly accurate and responsive. In a proportional control system, the output is proportional to the error, meaning that the closer the system is to the set point, the smaller the output will be. This type of system is also used to reduce the amount of overshoot and oscillations that can occur with other types of control systems.PID Controllers
PID control uses a combination of three distinct components to control the system: Proportional, Integral, and Derivative (hence the name ‘PID’). The proportional term is used to create an output that is proportional to the error, the integral term is used to eliminate any steady-state error, and the derivative term is used to provide damping and reduce the overshoot. The parameters of each of the PID terms are then adjusted to achieve the desired response.

PID Control
The third controller type provides proportional with integral and derivative control, or PID. This controller combines proportional control with two additional adjustments, which helps the unit automatically compensate for changes in the system.
These adjustments, integral and derivative, are expressed in time-based units; they are also referred to by their reciprocals, RESET and RATE, respectively. The proportional, integral and derivative terms must be individually adjusted or "tuned" to a particular system using trial and error. It provides the most accurate and stable control of the three controller types, and is best used in systems which have a relatively small mass, those which react quickly to changes in the energy added to the process.
In this other article, how to tune a PID controller is covered in more detail.
It is recommended in systems where the load changes often and the controller is expected to compensate automatically due to frequent changes in setpoint, the amount of energy available, or the mass to be controlled. OMEGA offers a number of controllers that automatically tune themselves. These are known as autotune controllers.
Standard Sizes
Since temperature controllers are generally mounted inside an instrument panel, the panel must be cut to accommodate the temperature controller. In order to provide interchangeability between temperature controllers, most temperature controllers are designed to standard DIN sizes. The most common DIN sizes are shown below.
Choose a temperature controller for your application

On-Off Controllers
On-Off process controllers are the simplest type of controllers featuring on-off control action designed to provide the functionality of general purpose PID controllers but at a price suited to On/Off applications.

Autotune PID Controllers
PID controllers provide very tight control but the PID algorithm requires tuning. Autotune controllers provide that function.
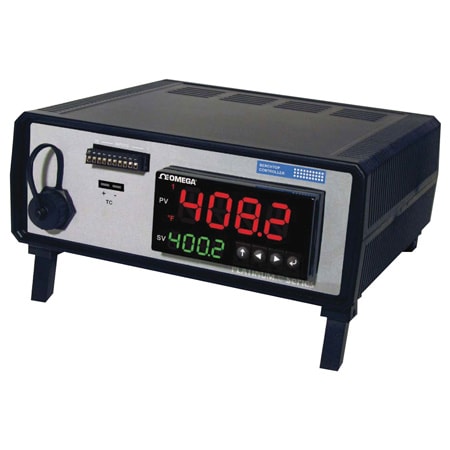

Multiloop Controllers
Each control loop normally consists of one input and at least one output. OMEGA offers numerous multiloop controllers which can handle more than a single control loop. OMEGA's CS8DPT can handle up to 6 control loops.
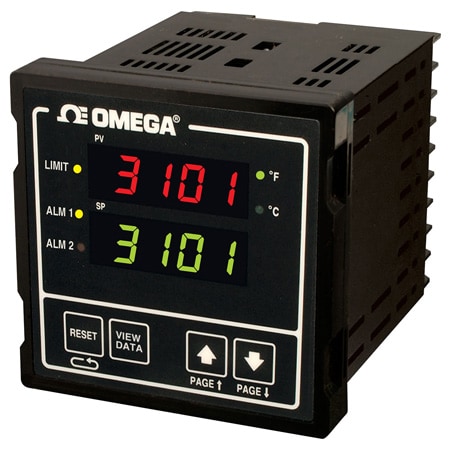

Safety Limit Controllers
A safety limit controller is an off-off controller with a latching output. When the output changes state it requires a manual reset to change it back. Safety limit controllers are typically used as redundant controllers, to shut down a process when undesirable limits are reached.

Common Uses in Industry
Digital temperature controllers are essential components used in a variety of industrial applications and are used to regulate and control temperatures within a system. These devices are designed to maintain a desired level of accuracy and precision and are often utilized in processes such as welding, soldering, injection molding, and food production.Some common uses of temperature controllers in industrial applications include:
- Refrigerators and Freezers: Temperature controllers are used to regulate the temperature of refrigerators and freezers to maintain a safe environment for food storage.
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC): Temperature controllers are used to control the temperature of air in a building or space to ensure occupant comfort.
- Ovens and Furnaces: Temperature controllers are used to regulate the temperature of ovens and furnaces to ensure that materials are heated or cooled to a desired temperature.
- Medical Facilities: Temperature controllers are used to regulate the temperature of incubators, medical refrigerators, and other medical devices.
- Chemical Processing: Temperature controllers are used to regulate the temperature of chemical processes to ensure the safety of workers and the quality of the end product.

