How does a data logger work?
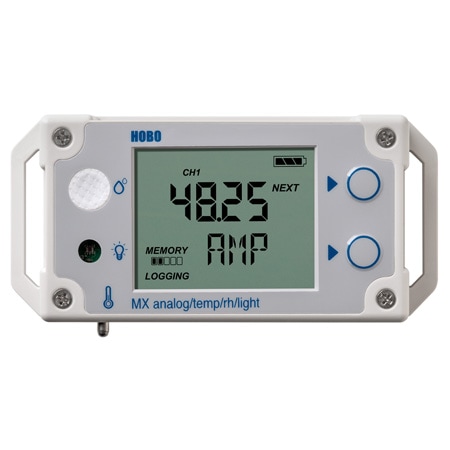
Data loggers use a microprocessor, an internal memory for data storage, and a sensor to collect data. They are generally small and battery powered devices.
Data loggers can either interface with a computer and use software to view and analyze the collected data or be used as a stand-alone device with a local interface. There are also wireless data loggers available.
The advantage of data loggers is that they can operate independently of a computer, unlike many other types of data acquisition devices. Data loggers are available in various shapes and sizes. The range includes simple economical single channel fixed function loggers to more powerful programmable devices capable of handling hundreds of inputs.
Data logger input types
Data loggers can accept different input types. There are also multi-input data loggers that can accept two or more types of input, such as temperature and humidity or temperature and pressure. Some data loggers can even accept all types of input.
The most common input types include:
- Pressure: Pressure data loggers measure the pressure of gases and liquids, including atmospheric and water pressure.
- Temperature: These loggers can be used to measure extremely high and low temperatures as well as liquid temperatures.
- Humidity: Humidity data loggers can collect data on relative humidity, dew point, and water vapor concentration in standard or metric units.
- Voltage: Voltage data loggers can adapt to any voltage measurement, including pressure to torque and load to force.
- Current: Current data loggers include a range of AC and DC data loggers and are often used to monitor building equipment.
Data logger applications
Data loggers can monitor temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, pH, pressure, voltage, current, and pulse – making them useful for a number of applications, including to:
- Verify temperature and humidity levels of storage and transportation facilities.
- Provide building maintenance information on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning operations to assist with energy conversavtion.
- Monitor growing conditions in the agricultural industry.
- Monitor vaccine storage in a medical facility.
- Monitor the temperature of food.
How long can data loggers record?
The recording duration depends on the memory capacity of the data logger and the desired sample rate. To determine the duration, divide the memory capacity (number of samples the device can record) by the sample rate. As an example, assume that a given data logger can store 10,000 samples. If you want to record two samples every minute, the data logger can run for 10,000/2 or 5,000 minutes (about 3.5 days).
How to retrieve data off your data logger
Depending on the type of data logger, you can either access the data directly within the data logger and even print it out, connect the data logger to a computer to extract the data, or data can be wirelessly transmitted in real-time to any connected device.
Data loggers are normally more economical than chart recorders. They offer more flexibility and are available with a greater variety of input types. Most data loggers collect data which may be directly transferred to a computer. Although this option is available with some recorders, it normally adds significant expense to the recorder price.
Data acquisition systems offer a great deal of flexibility and are certainly attractive when high sample rates are required. However, since they require connection or installation into a computer, the computer must also be present and active when collecting the data. Data loggers can collect data independently of a computer. Data is normally collected in non-volatile memory for later download to a computer. The computer does not need to be present during the data collection process. This makes them ideally suited for applications requiring portability.